Adaptive Wireless Sensor Networks with Data Visualization for Crisis Management
MPO CR – TIP (FR-TI2/571)
Project intent
The project aimed to design a modular communication system for adaptive wireless sensor networks (AWSN) with data visualization, which could be deployed for the needs of crisis management in solving extraordinary events of various character.
The subject of the project was mainly applied research on concepts of data acquisition from wireless sensors field nodes, their analysis, and visualization. The word “adaptable” was meant to be a system easily adaptable to various applications and scenarios, and thus a system that will be open to a certain extent for connecting different types and types of sensors, and other devices.
- Implementation period: 2010 – 2013
- Identification: FR-TI2/571
- Program: MPO CR – TIP
- Project role: Responsible investigator
- Co-researchers: VUT in Brno – Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication
- Related Links: WisLab (Wireless System Laboratory)
Project results
The result of the project solution was the design of the Komoris® integrated system based on the adaptable wireless sensor network (AWSN), consisting mainly of:
- radio modules for the creation of so-called mesh networks in the 868 MHz or 2.4 GHz band
- sensor units and gates to connect their sensors as well as other peripherals (e.g., beacons)
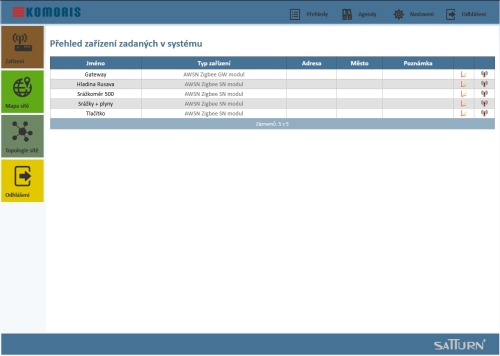
- supervisory SW Komoris with GIS support and crisis management outputs
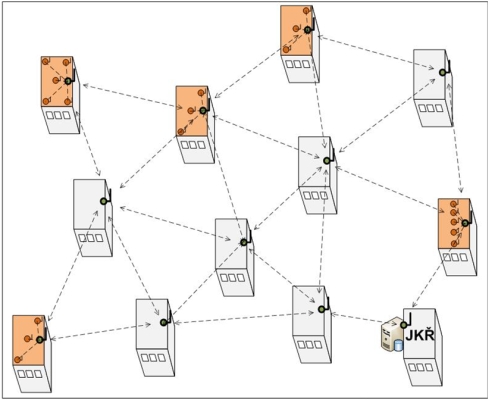
Communication technology is suitable for outdoor and indoor use and has been designed to allow simple ad-hoc networking, where radio links (paths) between individual sensor units, units, and gates, created automatically – the internal control logic of the units. Created networks then work completely automatically – without the need for control, for example, using a PC or other superior device, each of the sensor units being able to communicate simultaneously with all the units within its radio range (so-called mesh network). Network activity as a whole, therefore, with a sufficient number of installed units, is resistant to failures of one of the nodes.
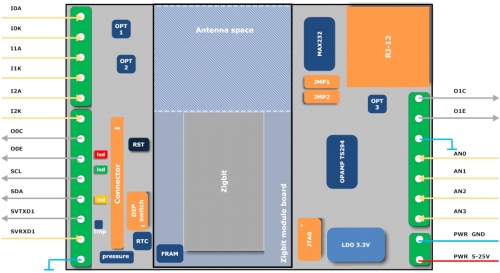
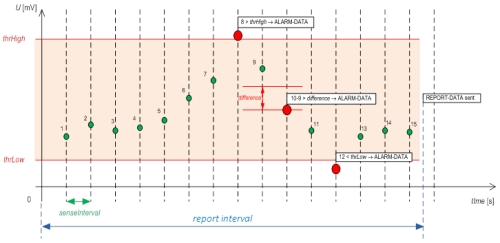
Sensor units are based on Zigbee radio technology. They allow the simultaneous connection of several sensors, controlling and reading data at set intervals or when exceeding the configurable ranges and limits, internal auto-diagnostics, over-the-air configuration, etc. All activity of units and communication within the network, receiving and processing of data packets) has been optimized for as low consumption as possible.
A separate chapter within the project was the research and development of a new type of snow-proof sensor for measuring the height and weight of a snow cover (not only) on the roofs of buildings. The design of the sensor is protected by a utility pattern.